- 浏览: 880563 次
-

文章分类
最新评论
-
mxdxm:
总结不错,赞
NoSQL学习笔记(三)之BigTable -
itbj00:
不错,有实际案例的文章,看着简单。
以公司实际应用讲解OpenStack到底是什么 -
追梦--:
赞一个!
数据库插入百万数据 -
enet_java:
<artifactId>PM_Member_EAR ...
使用maven2 打ear包
ARM-Linux驱动--DM9000网卡驱动分析(一)
硬件平台:FL2440(s3c2440)
内核版本:2.6.35
主机平台:Ubuntu11.04
内核版本:2.6.39
原创作品,转载请标明出处http://blog.csdn.net/yming0221/article/details/6609742
1、下图是DM9000的引脚图
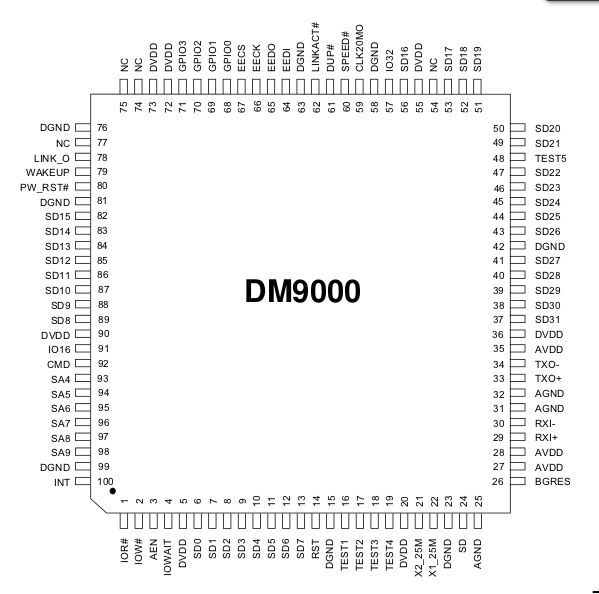
2、这里我们结合具体的开发板FL2440
下面是FL2440和DM9000的引脚链接图
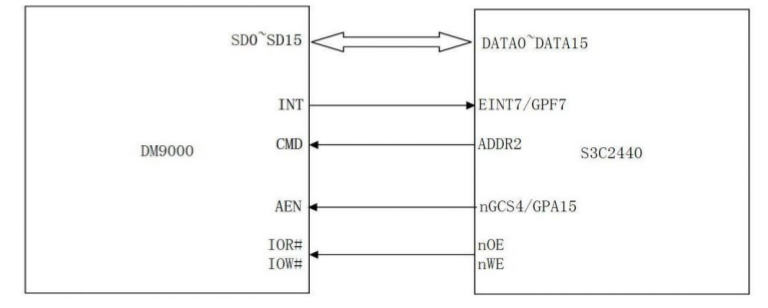
本人移植DM9000的时候将设备的资源定义放在了arch/arm/plat-s3c24xx/devs.c中,详情点击上一篇博文linux内核移植-移植2.6.35.4内核到s3c2440
下面是设备的资源定义
/*DM9000*/
/* 定义该设备使用的资源 */
static struct resource s3c_dm9000_resource[] = {
[0] = { /* 寄存器定义在mach-s3c2410/include/mach/map.h */
.start = S3C24XX_PA_DM9000, /* 实际地址 0x20000300 */
.end = S3C24XX_PA_DM9000+ 0x3, /* 0x20000303 */
.flags = IORESOURCE_MEM /* 资源标志为地址资源 */
},
[1]={
.start = S3C24XX_PA_DM9000 + 0x4, //CMD pin is A2 0x20000304
.end = S3C24XX_PA_DM9000 + 0x4 + 0x7c, // 0x20000380
.flags = IORESOURCE_MEM /* 资源标志为地址资源 */
},
[2] = {
.start = IRQ_EINT7, /* 中断为外部7号中断 */
.end = IRQ_EINT7, /* 中断为外部7号中断 */
.flags = IORESOURCE_IRQ /* 资源标志为中断资源 */
},
};
这里可以看到,DM9000网卡使用的地址空间资源在nGCS4地址区域,所以上图的DM9000地址使能引脚连接nGCS4引脚。中断使用的是EINT7外部中断。
接着定义平台数据和平台设备,代码如下:
/* 定义平台数据 */
static struct dm9000_plat_data s3c_device_dm9000_platdata = {
.flags= DM9000_PLATF_16BITONLY,
};
/* 定义平台设备 */
struct platform_device s3c_device_dm9000 = {
.name= "dm9000", //设备名,该名称与平台设备驱动中的名称一致
.id= 0,
.num_resources= ARRAY_SIZE(s3c_dm9000_resource),
.resource= s3c_dm9000_resource, //定义设备的资源
.dev= {
.platform_data = &s3c_device_dm9000_platdata, //定义平台数据
}
};
最后导出函数符号,保存函数地址和名称
EXPORT_SYMBOL(s3c_device_dm9000);
3、设备启动的初始化过程
MACHINE_START(S3C2440, "SMDK2440")
/* Maintainer: Ben Dooks <ben-linux@fluff.org> */
.phys_io = S3C2410_PA_UART,
.io_pg_offst = (((u32)S3C24XX_VA_UART) >> 18) & 0xfffc,
.boot_params = S3C2410_SDRAM_PA + 0x100,
.init_irq = s3c24xx_init_irq,/* 初始化中断 */
.map_io = smdk2440_map_io,
.init_machine = smdk2440_machine_init,//定义设备的初始化函数
.timer = &s3c24xx_timer,
MACHINE_END
而后会执行下面函数
static void __init smdk2440_machine_init(void)
{
s3c24xx_fb_set_platdata(&smdk2440_fb_info);
s3c_i2c0_set_platdata(NULL);
s3c24xx_ts_set_platdata(&smdk2410_ts_cfg);/* Added by yan */
platform_add_devices(smdk2440_devices, ARRAY_SIZE(smdk2440_devices));/* 向平台中添加设备 */
smdk_machine_init();
}
下面是具体的设备列表
static struct platform_device *smdk2440_devices[] __initdata = {
&s3c_device_ohci,
&s3c_device_lcd,/* ok */
&s3c_device_wdt,/* ok */
&s3c_device_i2c0,
&s3c_device_iis,
&s3c_device_rtc,/* ok */
&s3c24xx_uda134x,
&s3c_device_dm9000,
&s3c_device_adc,/* ok */
&s3c_device_ts,/* ok */
};
这样系统启动时,会给设备列表中的设备分配资源(地址资源和中断资源等)。
4、信息传输中的信息封装结构
4.1、sk_buff结构,定义在include/linux/skbuff.h中
struct sk_buff {
/* These two members must be first. */
struct sk_buff *next;
struct sk_buff *prev;
ktime_t tstamp;
struct sock *sk;
struct net_device *dev;
/*
* This is the control buffer. It is free to use for every
* layer. Please put your private variables there. If you
* want to keep them across layers you have to do a skb_clone()
* first. This is owned by whoever has the skb queued ATM.
*/
char cb[48] __aligned(8);
unsigned long _skb_refdst;
#ifdef CONFIG_XFRM
struct sec_path *sp;
#endif
unsigned int len,
data_len;
__u16 mac_len,
hdr_len;
union {
__wsum csum;
struct {
__u16 csum_start;
__u16 csum_offset;
};
};
__u32 priority;
kmemcheck_bitfield_begin(flags1);
__u8 local_df:1,
cloned:1,
ip_summed:2,
nohdr:1,
nfctinfo:3;
__u8 pkt_type:3,
fclone:2,
ipvs_property:1,
peeked:1,
nf_trace:1;
kmemcheck_bitfield_end(flags1);
__be16 protocol;
void (*destructor)(struct sk_buff *skb);
#if defined(CONFIG_NF_CONNTRACK) || defined(CONFIG_NF_CONNTRACK_MODULE)
struct nf_conntrack *nfct;
struct sk_buff *nfct_reasm;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_BRIDGE_NETFILTER
struct nf_bridge_info *nf_bridge;
#endif
int skb_iif;
#ifdef CONFIG_NET_SCHED
__u16 tc_index; /* traffic control index */
#ifdef CONFIG_NET_CLS_ACT
__u16 tc_verd; /* traffic control verdict */
#endif
#endif
__u32 rxhash;
kmemcheck_bitfield_begin(flags2);
__u16 queue_mapping:16;
#ifdef CONFIG_IPV6_NDISC_NODETYPE
__u8 ndisc_nodetype:2,
deliver_no_wcard:1;
#else
__u8 deliver_no_wcard:1;
#endif
kmemcheck_bitfield_end(flags2);
/* 0/14 bit hole */
#ifdef CONFIG_NET_DMA
dma_cookie_t dma_cookie;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_NETWORK_SECMARK
__u32 secmark;
#endif
union {
__u32 mark;
__u32 dropcount;
};
__u16 vlan_tci;
sk_buff_data_t transport_header;
sk_buff_data_t network_header;
sk_buff_data_t mac_header;
/* These elements must be at the end, see alloc_skb() for details. */
sk_buff_data_t tail;
sk_buff_data_t end;
unsigned char *head,
*data;
unsigned int truesize;
atomic_t users;
};
元素的含义如下(摘自内核,源码,版本2.6.35.4)
*struct sk_buff - socket buffer
* @next: Next buffer inlist
* @prev: Previous buffer in list
* @sk: Socketwe are owned by
* @tstamp: Time we arrived
* @dev:Device we arrived on/are leaving by
* @transport_header:Transport layer header
* @network_header: Network layerheader
* @mac_header: Link layer header
*@_skb_refdst: destination entry (with norefcount bit)
* @sp:the security path, used for xfrm
* @cb: Control buffer. Freefor use by every layer. Put private vars here
* @len: Lengthof actual data
* @data_len: Data length
* @mac_len:Length of link layer header
* @hdr_len: writable headerlength of cloned skb
* @csum: Checksum (must includestart/offset pair)
* @csum_start: Offset from skb->headwhere checksumming should start
* @csum_offset: Offset fromcsum_start where checksum should be stored
* @local_df:allow local fragmentation
* @cloned: Head may be cloned(check refcnt to be sure)
* @nohdr: Payload reference only,must not modify header
* @pkt_type: Packet class
*@fclone: skbuff clone status
* @ip_summed: Driver fed us anIP checksum
* @priority: Packet queueing priority
*@users: User count - see {datagram,tcp}.c
* @protocol:Packet protocol from driver
* @truesize: Buffer size
*@head: Head of buffer
* @data: Data head pointer
*@tail: Tail pointer
* @end: End pointer
*@destructor: Destruct function
* @mark: Generic packetmark
* @nfct: Associated connection, if any
*@ipvs_property: skbuff is owned by ipvs
* @peeked: thispacket has been seen already, so stats have been
* done forit, don't do them again
* @nf_trace: netfilter packet traceflag
* @nfctinfo: Relationship of this skb to theconnection
* @nfct_reasm: netfilter conntrack re-assemblypointer
* @nf_bridge: Saved data about a bridged frame - seebr_netfilter.c
* @skb_iif: ifindex of device we arrivedon
* @rxhash: the packet hash computed on receive
*@queue_mapping: Queue mapping for multiqueue devices
*@tc_index: Traffic control index
* @tc_verd: traffic controlverdict
* @ndisc_nodetype: router type (from link layer)
*@dma_cookie: a cookie to one of several possible DMA operations
*done by skb DMA functions
* @secmark: security marking
*@vlan_tci: vlan tag control information
关于sk_buff的更多分析见另一篇转载的博文http://blog.csdn.net/yming0221/article/details/6609734
4.2、net_device
关于net_device一个非常庞大的结构体,定义在/inlcude/linux/netdevice.h中
如下:
struct net_device {
/*
* This is the first field of the "visible" part of this structure
* (i.e. as seen by users in the "Space.c" file). It is the name
* the interface.
*/
char name[IFNAMSIZ];
struct pm_qos_request_list *pm_qos_req;
/* device name hash chain */
struct hlist_node name_hlist;
/* snmp alias */
char *ifalias;
/*
* I/O specific fields
* FIXME: Merge these and struct ifmap into one
*/
unsigned long mem_end; /* shared mem end */
unsigned long mem_start; /* shared mem start */
unsigned long base_addr; /* device I/O address */
unsigned int irq; /* device IRQ number */
/*
* Some hardware also needs these fields, but they are not
* part of the usual set specified in Space.c.
*/
unsigned char if_port; /* Selectable AUI, TP,..*/
unsigned char dma; /* DMA channel */
unsigned long state;
struct list_head dev_list;
struct list_head napi_list;
struct list_head unreg_list;
/* Net device features */
unsigned long features;
#define NETIF_F_SG 1 /* Scatter/gather IO. */
#define NETIF_F_IP_CSUM 2 /* Can checksum TCP/UDP over IPv4. */
#define NETIF_F_NO_CSUM 4 /* Does not require checksum. F.e. loopack. */
#define NETIF_F_HW_CSUM 8 /* Can checksum all the packets. */
#define NETIF_F_IPV6_CSUM 16 /* Can checksum TCP/UDP over IPV6 */
#define NETIF_F_HIGHDMA 32 /* Can DMA to high memory. */
#define NETIF_F_FRAGLIST 64 /* Scatter/gather IO. */
#define NETIF_F_HW_VLAN_TX 128 /* Transmit VLAN hw acceleration */
#define NETIF_F_HW_VLAN_RX 256 /* Receive VLAN hw acceleration */
#define NETIF_F_HW_VLAN_FILTER 512 /* Receive filtering on VLAN */
#define NETIF_F_VLAN_CHALLENGED 1024 /* Device cannot handle VLAN packets */
#define NETIF_F_GSO 2048 /* Enable software GSO. */
#define NETIF_F_LLTX 4096 /* LockLess TX - deprecated. Please */
/* do not use LLTX in new drivers */
#define NETIF_F_NETNS_LOCAL 8192 /* Does not change network namespaces */
#define NETIF_F_GRO 16384 /* Generic receive offload */
#define NETIF_F_LRO 32768 /* large receive offload */
/* the GSO_MASK reserves bits 16 through 23 */
#define NETIF_F_FCOE_CRC (1 << 24) /* FCoE CRC32 */
#define NETIF_F_SCTP_CSUM (1 << 25) /* SCTP checksum offload */
#define NETIF_F_FCOE_MTU (1 << 26) /* Supports max FCoE MTU, 2158 bytes*/
#define NETIF_F_NTUPLE (1 << 27) /* N-tuple filters supported */
#define NETIF_F_RXHASH (1 << 28) /* Receive hashing offload */
/* Segmentation offload features */
#define NETIF_F_GSO_SHIFT 16
#define NETIF_F_GSO_MASK 0x00ff0000
#define NETIF_F_TSO (SKB_GSO_TCPV4 << NETIF_F_GSO_SHIFT)
#define NETIF_F_UFO (SKB_GSO_UDP << NETIF_F_GSO_SHIFT)
#define NETIF_F_GSO_ROBUST (SKB_GSO_DODGY << NETIF_F_GSO_SHIFT)
#define NETIF_F_TSO_ECN (SKB_GSO_TCP_ECN << NETIF_F_GSO_SHIFT)
#define NETIF_F_TSO6 (SKB_GSO_TCPV6 << NETIF_F_GSO_SHIFT)
#define NETIF_F_FSO (SKB_GSO_FCOE << NETIF_F_GSO_SHIFT)
/* List of features with software fallbacks. */
#define NETIF_F_GSO_SOFTWARE (NETIF_F_TSO | NETIF_F_TSO_ECN | NETIF_F_TSO6)
#define NETIF_F_GEN_CSUM (NETIF_F_NO_CSUM | NETIF_F_HW_CSUM)
#define NETIF_F_V4_CSUM (NETIF_F_GEN_CSUM | NETIF_F_IP_CSUM)
#define NETIF_F_V6_CSUM (NETIF_F_GEN_CSUM | NETIF_F_IPV6_CSUM)
#define NETIF_F_ALL_CSUM (NETIF_F_V4_CSUM | NETIF_F_V6_CSUM)
/*
* If one device supports one of these features, then enable them
* for all in netdev_increment_features.
*/
#define NETIF_F_ONE_FOR_ALL (NETIF_F_GSO_SOFTWARE | NETIF_F_GSO_ROBUST | \
NETIF_F_SG | NETIF_F_HIGHDMA | \
NETIF_F_FRAGLIST)
/* Interface index. Unique device identifier */
int ifindex;
int iflink;
struct net_device_stats stats;
#ifdef CONFIG_WIRELESS_EXT
/* List of functions to handle Wireless Extensions (instead of ioctl).
* See <net/iw_handler.h> for details. Jean II */
const struct iw_handler_def * wireless_handlers;
/* Instance data managed by the core of Wireless Extensions. */
struct iw_public_data * wireless_data;
#endif
/* Management operations */
const struct net_device_ops *netdev_ops;
const struct ethtool_ops *ethtool_ops;
/* Hardware header description */
const struct header_ops *header_ops;
unsigned int flags; /* interface flags (a la BSD) */
unsigned short gflags;
unsigned short priv_flags; /* Like 'flags' but invisible to userspace. */
unsigned short padded; /* How much padding added by alloc_netdev() */
unsigned char operstate; /* RFC2863 operstate */
unsigned char link_mode; /* mapping policy to operstate */
unsigned int mtu; /* interface MTU value */
unsigned short type; /* interface hardware type */
unsigned short hard_header_len; /* hardware hdr length */
/* extra head- and tailroom the hardware may need, but not in all cases
* can this be guaranteed, especially tailroom. Some cases also use
* LL_MAX_HEADER instead to allocate the skb.
*/
unsigned short needed_headroom;
unsigned short needed_tailroom;
struct net_device *master; /* Pointer to master device of a group,
* which this device is member of.
*/
/* Interface address info. */
unsigned char perm_addr[MAX_ADDR_LEN]; /* permanent hw address */
unsigned char addr_len; /* hardware address length */
unsigned short dev_id; /* for shared network cards */
spinlock_t addr_list_lock;
struct netdev_hw_addr_list uc; /* Unicast mac addresses */
struct netdev_hw_addr_list mc; /* Multicast mac addresses */
int uc_promisc;
unsigned int promiscuity;
unsigned int allmulti;
/* Protocol specific pointers */
#ifdef CONFIG_NET_DSA
void *dsa_ptr; /* dsa specific data */
#endif
void *atalk_ptr; /* AppleTalk link */
void *ip_ptr; /* IPv4 specific data */
void *dn_ptr; /* DECnet specific data */
void *ip6_ptr; /* IPv6 specific data */
void *ec_ptr; /* Econet specific data */
void *ax25_ptr; /* AX.25 specific data */
struct wireless_dev *ieee80211_ptr; /* IEEE 802.11 specific data,
assign before registering */
/*
* Cache line mostly used on receive path (including eth_type_trans())
*/
unsigned long last_rx; /* Time of last Rx */
/* Interface address info used in eth_type_trans() */
unsigned char *dev_addr; /* hw address, (before bcast
because most packets are
unicast) */
struct netdev_hw_addr_list dev_addrs; /* list of device
hw addresses */
unsigned char broadcast[MAX_ADDR_LEN]; /* hw bcast add */
#ifdef CONFIG_RPS
struct kset *queues_kset;
struct netdev_rx_queue *_rx;
/* Number of RX queues allocated at alloc_netdev_mq() time */
unsigned int num_rx_queues;
#endif
struct netdev_queue rx_queue;
struct netdev_queue *_tx ____cacheline_aligned_in_smp;
/* Number of TX queues allocated at alloc_netdev_mq() time */
unsigned int num_tx_queues;
/* Number of TX queues currently active in device */
unsigned int real_num_tx_queues;
/* root qdisc from userspace point of view */
struct Qdisc *qdisc;
unsigned long tx_queue_len; /* Max frames per queue allowed */
spinlock_t tx_global_lock;
/*
* One part is mostly used on xmit path (device)
*/
/* These may be needed for future network-power-down code. */
/*
* trans_start here is expensive for high speed devices on SMP,
* please use netdev_queue->trans_start instead.
*/
unsigned long trans_start; /* Time (in jiffies) of last Tx */
int watchdog_timeo; /* used by dev_watchdog() */
struct timer_list watchdog_timer;
/* Number of references to this device */
atomic_t refcnt ____cacheline_aligned_in_smp;
/* delayed register/unregister */
struct list_head todo_list;
/* device index hash chain */
struct hlist_node index_hlist;
struct list_head link_watch_list;
/* register/unregister state machine */
enum { NETREG_UNINITIALIZED=0,
NETREG_REGISTERED, /* completed register_netdevice */
NETREG_UNREGISTERING, /* called unregister_netdevice */
NETREG_UNREGISTERED, /* completed unregister todo */
NETREG_RELEASED, /* called free_netdev */
NETREG_DUMMY, /* dummy device for NAPI poll */
} reg_state:16;
enum {
RTNL_LINK_INITIALIZED,
RTNL_LINK_INITIALIZING,
} rtnl_link_state:16;
/* Called from unregister, can be used to call free_netdev */
void (*destructor)(struct net_device *dev);
#ifdef CONFIG_NETPOLL
struct netpoll_info *npinfo;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_NET_NS
/* Network namespace this network device is inside */
struct net *nd_net;
#endif
/* mid-layer private */
void *ml_priv;
/* bridge stuff */
struct net_bridge_port *br_port;
/* macvlan */
struct macvlan_port *macvlan_port;
/* GARP */
struct garp_port *garp_port;
/* class/net/name entry */
struct device dev;
/* space for optional device, statistics, and wireless sysfs groups */
const struct attribute_group *sysfs_groups[4];
/* rtnetlink link ops */
const struct rtnl_link_ops *rtnl_link_ops;
/* VLAN feature mask */
unsigned long vlan_features;
/* for setting kernel sock attribute on TCP connection setup */
#define GSO_MAX_SIZE 65536
unsigned int gso_max_size;
#ifdef CONFIG_DCB
/* Data Center Bridging netlink ops */
const struct dcbnl_rtnl_ops *dcbnl_ops;
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_FCOE) || defined(CONFIG_FCOE_MODULE)
/* max exchange id for FCoE LRO by ddp */
unsigned int fcoe_ddp_xid;
#endif
/* n-tuple filter list attached to this device */
struct ethtool_rx_ntuple_list ethtool_ntuple_list;
};
我还没有细细的分析这个结构体,驱动程序在probe函数中使用register_netdev()注册该结构体指明的设备,将内核操作硬件的函数个内核联系起来。
更多见下一节分析ARM-Linux驱动--DM9000网卡驱动分析(二)






相关推荐
arm9开发板上 dm9000网卡驱动程序分析
linux dm9000网卡完全驱动 实现基本的网络通信经过大量测试 适合移植使用
研究分析了Linux内核中经典的bus-device-driver框架结构及Linux内核中提供的输入子系统框架,以及LCD、触摸屏、网卡、摄像头驱动框架等,分别设计并实现了LCD、触摸屏、摄像头、按键四种设备驱动程序,并对DM9000网卡...
1. 移植DM9000网卡驱动 之前配置使用的SMDK2440开发板,默认不支持DM9000网卡驱动,但是其中的MINI2440开发板支持,所以要将MINI2440中的DM9000驱动移植到SMDK2440中。 进入内核源码目录里面,找到 arch/arm/mach-s3...
本文主要介绍单片机驱动DM9000E网卡芯片的详细过程。从网卡电路的连接,到网卡初始化相关程序调试,再到ARP协议的实现,一步一步详细介绍调试过程。如果有时间也会把UDP和TCP通讯实验过程写出来。当然,会用单片机...
linux2.6.28 开发板:飞凌TE6410 (256M RAM 2G NAND) 网卡:ENC28J60 SPI 测试用的工具:Saleae logic (逻辑分析仪),Iris 抓包工具 6410作为一颗强大的ARM11处理器,网卡模块已经是相当的成熟(如:DM9000/3 ...
·嵌入式Linux之我行——Linux-2.6.30.4在2440上的移植之DM9000E网卡驱动 ·嵌入式Linux之我行——Linux-2.6.30.4在2440上的移植之USB驱动 ·嵌入式Linux之我行——Linux-2.6.30.4在2440上的移植之MMC/SD卡驱动 ·...
linux2.6.28 开发板:飞凌TE6410 (256M RAM 2G NAND) 网卡:ENC28J60 SPI 测试用的工具:Saleae logic (逻辑分析仪),Iris 抓包工具 6410作为一颗强大的ARM11处理器,网卡模块已经是相当的成熟(如:DM9000/3 ...
1 引言要实现小型嵌入式设备的Internet接入,TCP/IP首先要解决的是底层硬件问题,即协议的物理层。Ethernet具有成熟的技术...寄存器操作简单有效,有成熟的Linux驱动程序支持;3.3V接口电平;成本相当低廉;还可以使用
涵盖2.6.36内核和文件系统搭建...注意:arm-none-linux-guneabi version 4.5.2;NAND FLASH 256M (SLC);DM9000 的网卡;yaffs2 文件系统。NAND FLASH是SLC 256M,并非MLC 2G,否则需要修改相应的nand flash 驱动。
10/100M以太网卡DM9000驱动 以太网口2 CPU内部自带MAC层的以太网驱动 LCD 320x240,480x272,640x480,800x480四种屏的驱动 touch screen 触摸屏驱动 音频 音频驱动 MMC/SD SDIO模式驱动 USB host 可支持USB接口的...
介绍了一种基于ARM的综采面无线传感器网络的网关设计。...阐述了网关的硬件设计,重点论述了无线收发模块和以太网接口模块,并介绍了DM9000以太网卡的移植,CC2420无线模块驱动的开发,以及上层应用程序等软件设计。